Freshness Retention Catalyst (Ethylene Removal)

| Model | NFK Series |
|---|

Product Overview
This product is a freshness-retaining catalyst that uses palladium (Pd) as its active material. The catalyst is constructed using a three-dimensional honeycomb structure to increase the geometric surface area. By incorporating the precious metal palladium (which is often used in treatments for odorous gasses) on the surface of the catalyst, the ethylene generated from food products is caught and broken down into CO2 and H2O. When ethylene is removed from the air, fruits and vegetables will ripen more slowly and retain their freshness longer.
Features

Specifications
Compatible with any size.
*Please specify the intended use for the product.
Use
Works as a filter for the breakdown of ethylene in refrigerators and other containers.
Why do fruits and vegetables spoil?
Fruits and vegetables secrete a component called ethylene gas. Ethylene gas is a type of plant hormone that is responsible for the sweetness and bright colors that indicate the ripening of fruits and vegetables.
However, if left for too long, this gas becomes the main cause for wilting and spoilage. The ethylene gas that is released into the air affects not only the fruits and vegetables that secrete it, but also the surrounding produce.
If other produce is placed in the same refrigerator compartment as items that secrete high levels of ethylene gas, such as apples and tomatoes, this surrounding produce will ripen and wilt faster than usual.

How can we make fruits and vegetables last longer?
To prevent wilting and maintain the freshness of fruits and vegetables, ethylene gas must be removed. There are two main methods to remove ethylene. The first is to absorb it in porous materials such as zeolite or activated charcoal. Another method is to promote an oxidation reaction by utilizing the oxidizing power of potassium permanganate (KMnO4). As zeolite and activated charcoal prevent reactions until the absorption sites are saturated, and potassium permanganate prevents reactions while it is being consumed, both methods are effective for short-term ethylene removal. However, when aiming for long-term freshness retention, such as in refrigerators, the catalyst method is most effective.
How ethylene is removed using catalysts
The catalyst utilizes oxygen from the surrounding air to oxidize ethylene, ultimately converting the ethylene into CO2 and H2O which are then dispersed harmlessly into the air.
*Illustration of the Freshness Retention Catalyst in use
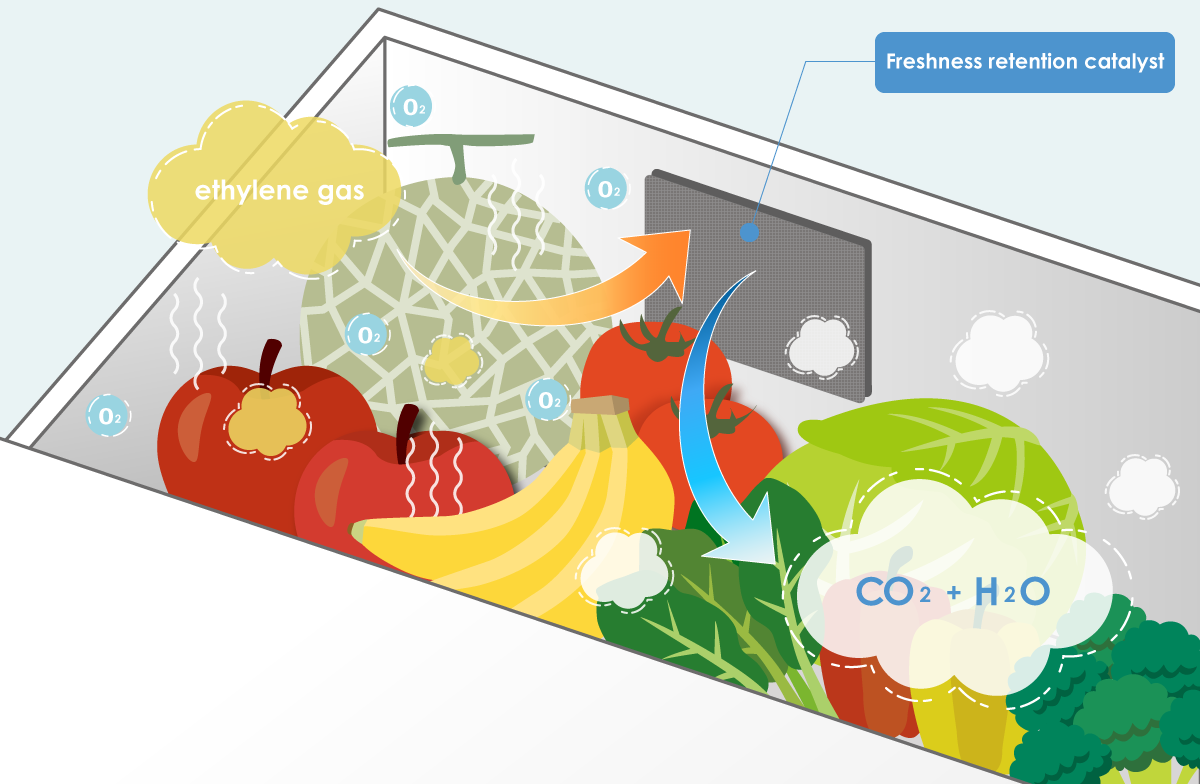
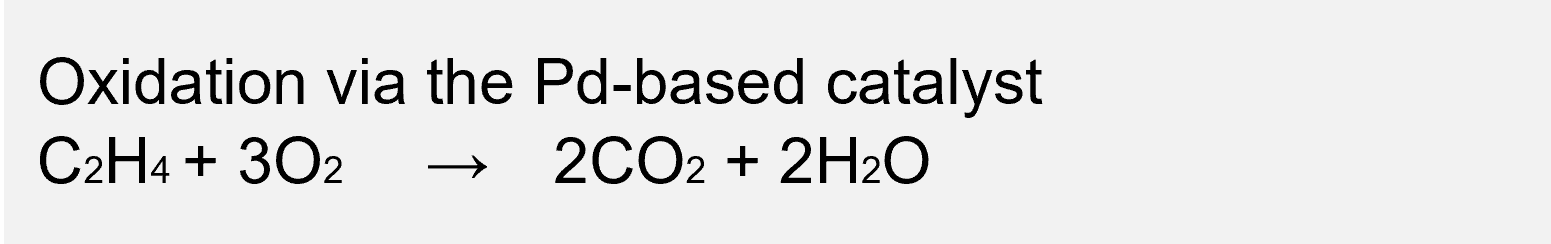
*The Pd-based catalyst reaction is an extension of the Wacker oxidation reaction that produces acetaldehyde industrially. By way of acetaldehyde (CH3CHO), the bonds of C2H4 are cleaved to become CO2 and H2O, which are harmless.
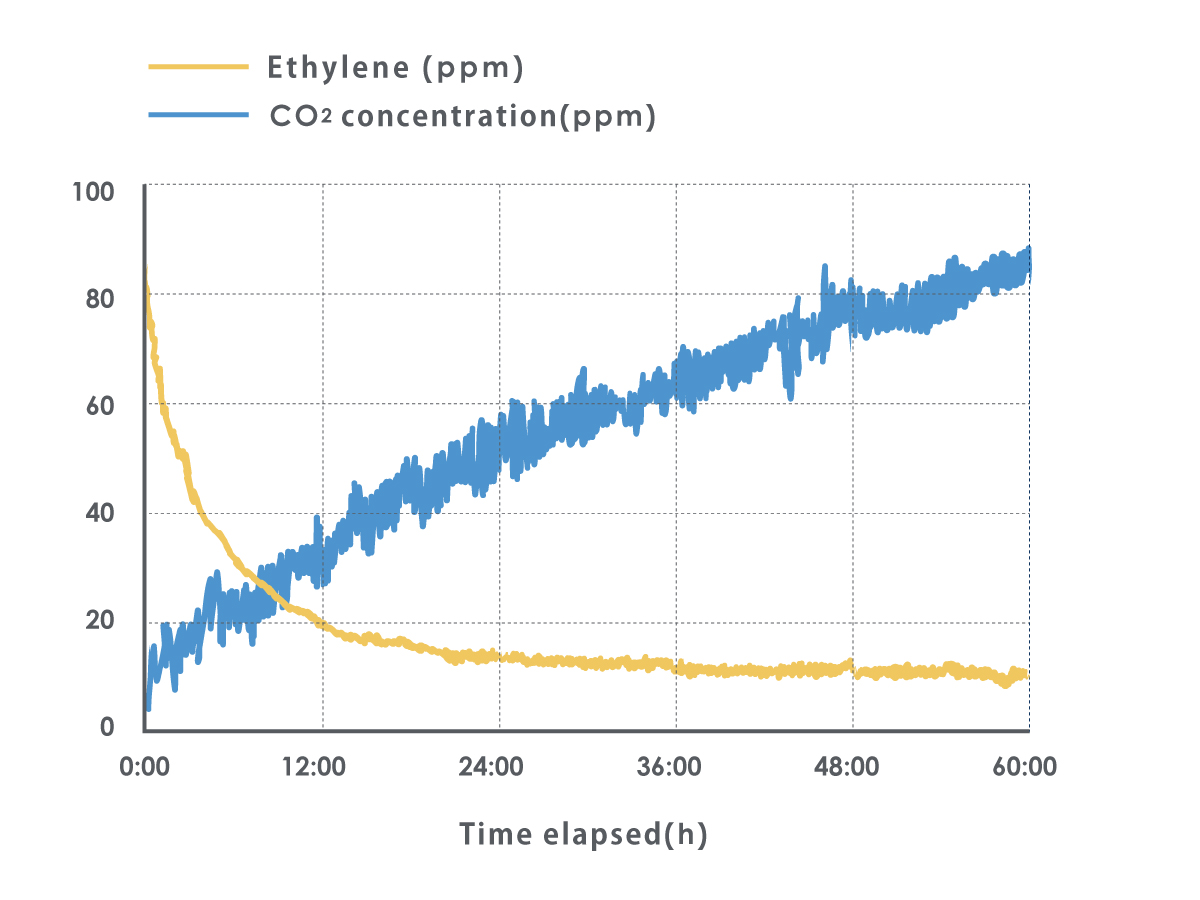
Additionally, the catalyst method reacts quickly to ethylene gas in order to break it down. The reaction speed is approximately 0.1 seconds when used at high temperatures (around 200oC), and around 0.5~2 seconds when used in low temperatures, such as inside a refrigerator.
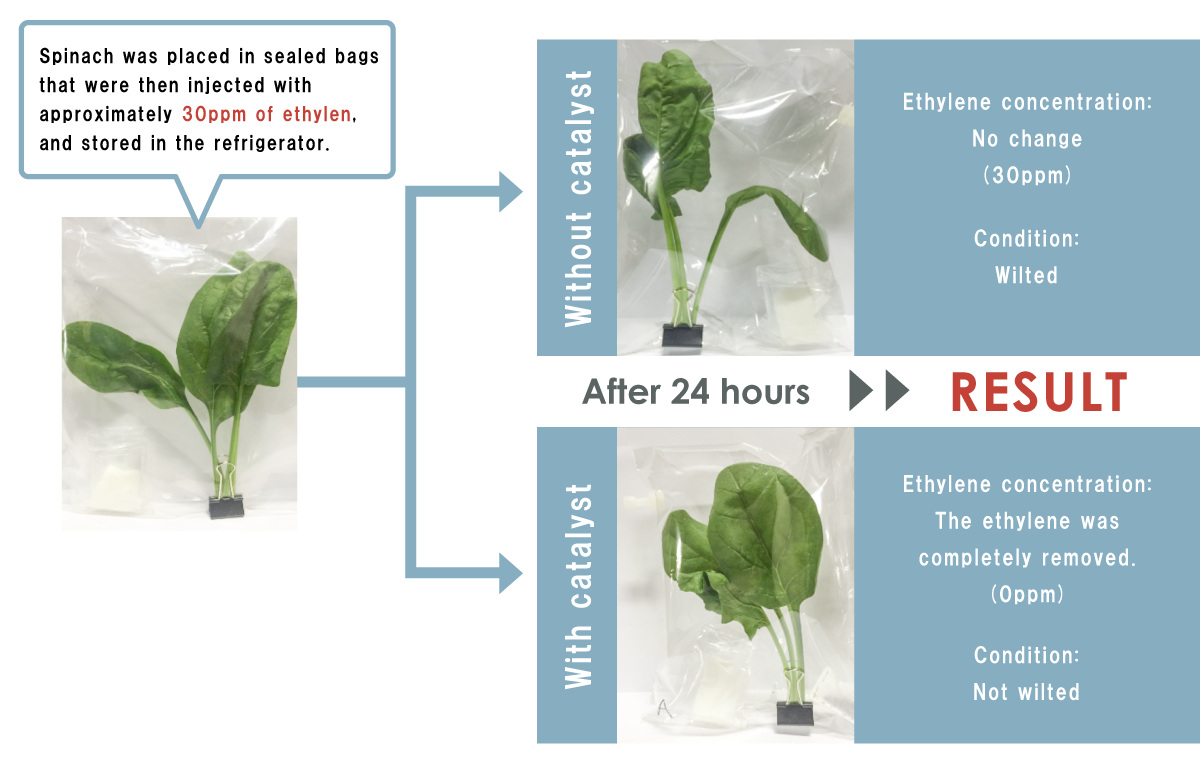
What differences in freshness emerge when ethylene gas is removed?
Test conditions: lettuce was placed in sealed bags that were then injected with approximately 20ppm of ethylene a total of five times at regular intervals.

Contact Sales Department
| Department | Environmental Catalyst Div. |
|---|---|
| Contact Form | |
| TEL | 81-3-5436-8484 |
| FAX | 81-3-5436-8680 |