Catalyst Poison Countermeasures
The most common cause of catalyst performance decline is catalyst poisoning caused by substances called catalyst poisons. One of the key factors affecting catalyst performance and catalyst life is the type and concentration of the catalyst poisons.
The following table introduces the typical catalyst poisons and their general countermeasures.

| Catalyst poison | Mechanism | Degree | Countermeasure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid materials (dust, rust, etc.) | Physical coating over the catalyst surface (temporary poisoning) | Low | Air blowing. Filtration upstream of the catalyst bed. |
| Mist (Tar, resin, etc.) | Physical coating over the catalyst surface (temporary poisoning) | High | Air-combustion treatment (decoking). Installation of a demister upstream of the catalyst bed. |
| Organic silicones, organic phosphorus (siloxane, organic phosphate, etc.) | Chemically acts on the catalyst (permanent poisoning) | High | Installation of guard bed catalysts (pre-treaters) upstream of the catalyst bed. Application of poisoning resistant catalysts. Rejuvenation of the catalysts. |
| Organic metal compounds (Hg, Pb, Zn, Sb, etc.) | Chemically acts on the catalyst (permanent poisoning) | High | Installation of guard bed catalysts (pre-treaters) upstream of the catalyst bed. |
| Sulfur compounds (H2S, COS, SO2, etc.) | Chemically acts on the catalyst (permanent poisoning) | Moderate | Application of sulfur resistant catalysts. |
| Halogens compounds (F, Cl, Br, etc.) | Usually the poisoning effect is observable only while in contact with halogens, however, in case of high concentration and/or long-term exposure it can permanently poison the catalyst (temporary or permanent poisoning) | Moderate | Increasing the catalyst inlet temperature. Application of halogen resistant catalysts. |
| Water content | Similar to thermal sintering under high water content and high temperature (permanent poisoning) | Moderate | - |
Solid materials (rust, dust, etc.)
Although it varies depending on the shape and properties of the substance, it generally has little effect on the catalyst performance.
Measures
Installation of a filter on the upstream side of the catalyst bed to reduce the dispersed amount.
Removing of the adhering particles (by air blow for example).
The maximum allowable dust amount in the exhaust gas is 5 mg/Nm3.


Mist (tar, resins, etc.)
The tar-like substances dispersed from painting and drying processes are mainly derived from paint. These substances are gaseous when generated in the drying ovens, but become mist or solid as they cool down by reaching the catalyst bed. If the catalytic reaction temperature is low, the oxidation-combustion process will not be complete and carbonated deposit will form on the catalyst surface, declining its performance.
Measures
Combustion of the adhering carbonated deposit.

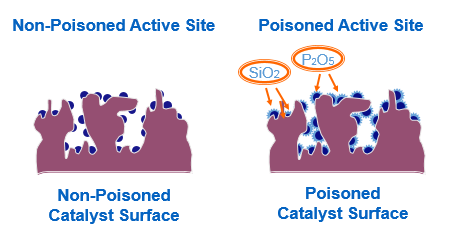
Organic silicones, organic phosphorus, organic metal compounds
When organic silicones, organic phosphorus, and organic metal compounds are heated and vaporized, while reaching the catalyst bed, they selectively bond with the active metal sites present on the catalyst (platinum, palladium, etc.) and become a non-volatile oxide overlaying those sites. Even at extremely low concentrations (ppb order), it leads to a decline in the catalytic performance.
Measures
- Guard-bed catalysts (pre-treater): by installing such pre-treaters on the upstream side of the catalyst bed, catalyst poisons are captured and the catalysts are protected.
- Poisoning-resistant catalysts: catalysts with poisoning-resistant functions.
- Rejuvenation of the catalysts: we use our original technology to restore the performance of the poisoned catalysts.
Halogen compounds
Regardless of whether they are inorganic or organic, they can affect catalyst performance even at very low concentrations (ppm order). The effect on the catalysts changes depending on the concentration of the halogen compounds. If the concentration is low, catalyst performance will drop due to the temporary adsorption of halogens. Once the halogen compounds are no longer present in the gas stream, the catalytic performance tends to recover.
Measures
- Poisoning-resistant catalysts: catalysts with poisoning-resistant functions.
Sulfur compounds
In typical oxidation catalysts, sulfur compounds are oxidized into SOx compounds, which corrode the catalyst itself and causes fatal damage to the catalyst in a short period of time. If the concentration is low, it can be faced by an elevation of the reaction temperature or by increasing the amount of catalyst. However, if the concentration is as high as several hundred ppm, the remaining sulfur on the catalyst cannot be removed easily and the poisoning will be permanent. The catalyst components might start to partially fall off.
Measures
- Poisoning-resistant catalysts: catalysts with poisoning-resistant functions.
For inquiries:
| Department | Environmental Catalyst Div. |
|---|---|
| Contact Form | |
| TEL | ARIOKA:+81-90-5398-5199 (Japanese, English) PIET:+81-80-4462-6530 (French, English) *Do not hesitate to reach out to us by using the contact form, we will come back to you as soon as possible. |
